How is a injection mold made?
We are frequently asked how we manufacture injection mold, and more specifically how do we do it. To answer this, it helps to put our services into context. The cost and time required to produce traditional high-volume production injection mold tooling are a consequence of needing to maximize productivity and minimize per part costs for large production volumes. Very high volumes and high production rates dictate hardened steel tooling with full automation, multiple cavities, and advanced runner and cooling systems. Such tools are complex, time-consuming to produce and test, and even more difficult to modify once in operation. However, when the customer requires a few hundred injections molded components on a tight delivery schedule, and the rate of production is not required to be high, a completely different mold production approach can be employed.
Understanding customer requirements are the foundation for every successful injection mold project
From the very outset of every client engagement, we strive to understand the full context of the project we are producing molded components for, to be sure we are addressing the customer’s primary needs, and are making the best decisions for the mold design. For example:
- What is the end-use of the product?
- What do the components we are molding do?
- Will components be used for form, fit, function testing?
- Is the project only a model for a coming trade show?
- Are the components intended as end-use production parts?
- How was the requested material chosen and what were the requirements?
- Do the components need to have a high-quality surface finish or special texture?
- Will the customer need 25 components in a few days or 250,000 over the next few months?
Understanding and acting on the answers to each of these questions are the foundation of a successful injection molding project.
Translating requirements into fast action
Once we have gathered the requisite contextual information, our engineering and design team initiate an extremely tightly managed process of converting requirements and 3D CAD data into a mold proposal. Even at this early stage, the project is already being managed by our proprietary design to assure efficient execution at every stage downstream. This is essential, in that it assures that everything quoted can be designed, machined, and molded efficiently to meet our very short delivery timelines. Mold design engineers take into consideration the specific characteristics of the molded polymer, the required production volume and rate, and the per-part cost objectives of the customer.
Form follows function when designing an injection mold
Even within the sub-category of prototype and low volume injection molding, there are many choices to be made on specifically how each mold is to function. In the case of very simple low volume components in a forgiving material, the mold would be a simple single cavity open and close design. When undercuts are required the designer will consider current and future production volumes to decide if the tool will be automated or include hand-loaded inserts for these features. The use of hand-loaded inserts reduces the cost and production time of the mold but generally increases the per-part cost due to the manual tending of the molding machine. Finally, in the case of complex geometries, including inserts and over-molded features in multiple materials, the full spectrum of design concepts will be deployed to balance product needs with cost and delivery time constraints.
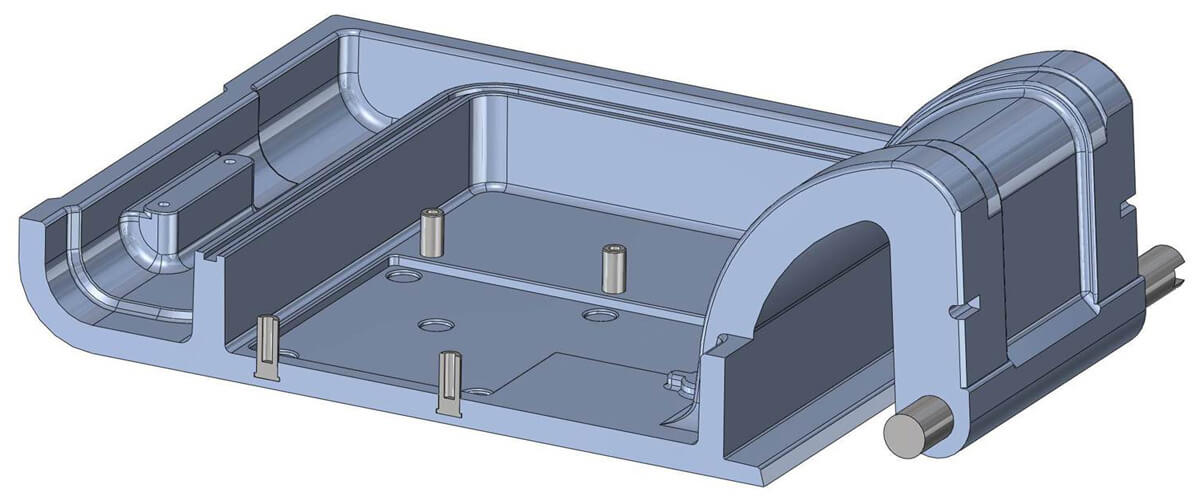
Design validation in electrons, not metal
Following initial mold design, our team performs mold flow analysis to reduce the likelihood of problems in the molding process. Depending on the complexity of the molded component, this can be a simple filling simulation all the way to complex warpage and shrinkage analysis, fiber orientation estimates for filled polymers, and other factors. Catching issues and collaborating closely with our clients at this stage to resolve potential problems leads to better products and higher on-time-delivery rates. Although we are quite nimble in rectifying problems that arise in the molding process, it is far easier and more efficient to do this when the mold is still in CAD and not in the press. Ultimately the completed mold design is reviewed with the client for approval prior to production.
Preparing for production
Once the mold design is complete, the process starts to really accelerate. The individual components of the mold (core, cavity, inserts, actions, ejector pins, etc.) are designated for their respective manufacturing process: CNC machining, EDM (electrical discharge machining), grinding, and manual machining.
The expert finishing touches complete the injection mold build process
Production of high-quality injection molds will always demand the personal attention of expert mold makers. At CHT we have a team of highly talented and hugely experienced mold makers who finish and test every mold to assure proper functioning of the mold and to achieve the desired surface finish of the molded components. This is part engineering and part artistry and cannot be rushed. So, all of the efficiency we build into the prior mold production steps assures that this team has enough time to do the mold finishing process properly. Naturally we do everything possible to maximize the mold surface finish quality coming out of CNC and EDM so that manual finishing or laser texturing is less difficult. Finally, the various components of the mold are all brought together in the assembly department where the functional mold is built up and tested prior to delivery to the molding department.




